How to Stop Thinning Hair in Women: Complete Guide
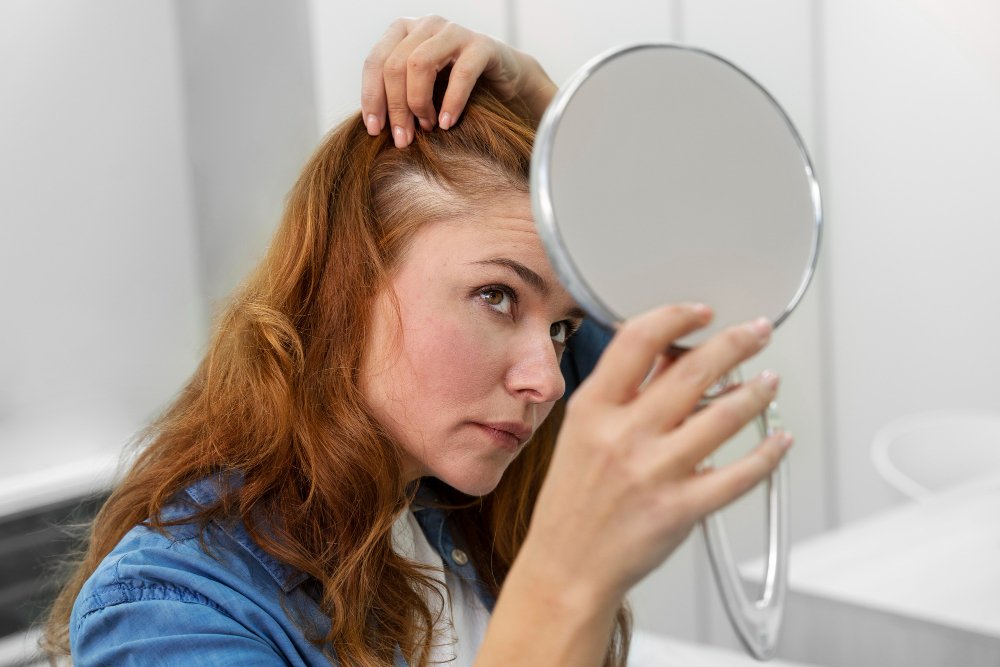
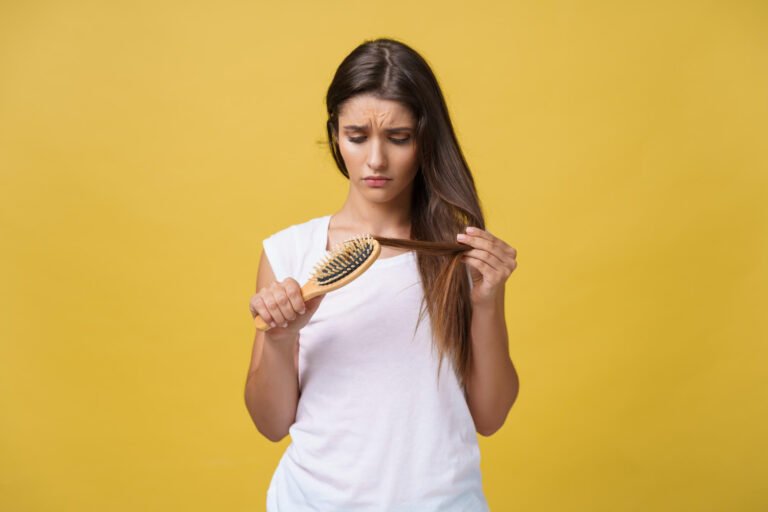
Noticing more hair than usual in your brush or a slightly wider part can be unsettling. Hair thinning is a common issue, with more than half of all women experiencing noticeable hair loss at some point. While it’s a widespread concern, understanding the causes and available solutions can empower you to take control.
This guide will walk you through why hair thinning happens, from lifestyle habits to medical conditions, and explore effective treatments and preventative measures. By understanding the root of the issue, you can find the right path to restoring your hair’s health and volume.
Why Is My Hair Thinning?
Hair loss in women can be complex, stemming from a variety of factors. Identifying the specific cause is the first step toward finding an effective solution. A dermatologist can provide a definitive diagnosis, but here are some of the most common culprits.
Medical Conditions and Hormonal Changes
Your overall health is directly linked to the health of your hair. Several medical issues can lead to thinning hair:
- Hormonal Shifts: Events like pregnancy, stopping birth control pills, and menopause can disrupt hormone levels, causing hair follicles to shrink and hair to thin.
- Thyroid Problems: An underactive or overactive thyroid can interfere with the hair growth cycle.
- Anemia and Vitamin Deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients like iron, vitamin D, zinc, and folic acid can weaken hair and lead to shedding. According to Healthline, deficiencies in riboflavin and selenium can also contribute.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus or certain skin disorders can cause inflammation that affects the scalp and hair follicles.
Genetics (Androgenetic Alopecia)
Often called female-pattern hair loss (FPHL), this is a hereditary condition that affects approximately 30 million women in the United States, according to the Cleveland Clinic. It typically manifests as a widening part on the top of the head and can begin as early as a woman’s 40s or 50s.
Lifestyle Factors
Daily habits and significant life events can also play a major role in the health of your hair.
- Stress: Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can trigger a type of hair loss known as telogen effluvium, where a large number of hairs enter the shedding phase at once.
- Diet and Weight Loss: Rapid weight loss or a diet lacking in essential proteins, vitamins, and minerals can shock the system and lead to temporary hair shedding.
- Harsh Hairstyles and Treatments: Frequently wearing tight hairstyles that pull on the follicles (like tight ponytails or braids) can cause breakage. Similarly, overuse of chemical treatments like dyes, perms, and relaxers can damage the hair shaft and scalp.
Medications
Certain medications and medical treatments can have hair loss as a side effect. These include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, some blood pressure medicines, and high doses of vitamin A.
Treatments for Thinning Hair in Women
Once you and your healthcare provider have identified the cause of your hair thinning, you can explore various treatment options. These range from over-the-counter products to medical procedures.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Solutions
- Minoxidil (Rogaine®): This is one of the most well-known and widely used treatments. Available in 2% or 5% solutions, Minoxidil is applied directly to the scalp to stimulate hair follicles and encourage regrowth.
- Anti-Thinning Shampoos: These products often work by adding volume to the hair, making it appear thicker. Some also contain nutrients and amino acids to promote a healthier scalp environment.
- Vitamins and Supplements: If a deficiency is the cause, supplements can be highly effective. Look for multivitamins containing iron, folic acid, and zinc. Biotin and omega-3 fatty acids are also popular for supporting hair health, although it’s best to consult a doctor before starting any new supplement.
Prescription Medications
For more persistent hair loss, a doctor might prescribe stronger medications:
- Spironolactone: An anti-androgen drug that can be effective for hair loss related to hormonal imbalances.
- Finasteride: While more commonly prescribed for men, it is sometimes used off-label for women.
- Corticosteroids: These can be prescribed to reduce inflammation associated with certain scalp conditions that cause hair loss.
Clinical Procedures and Therapies
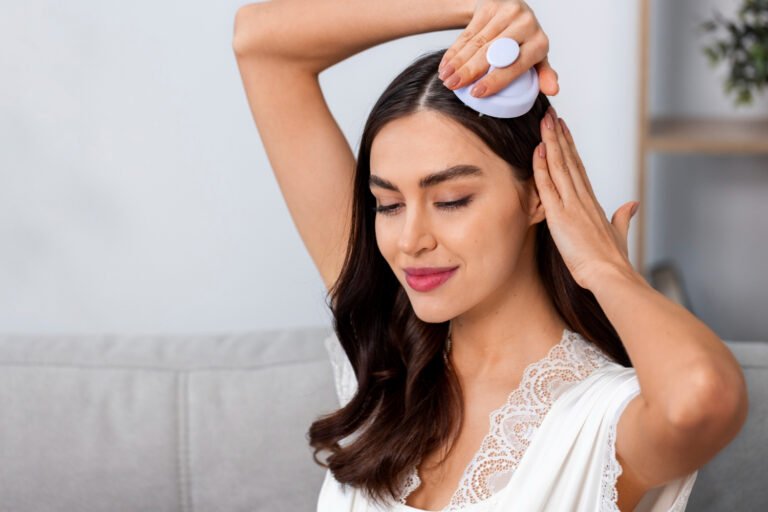
- Light Therapy: Devices like the HairMax Lasercomb® or Theradome LH80 PRO® helmet use low-level laser light to stimulate hair follicles and promote growth.
- Microneedling: This procedure involves using fine needles to create tiny punctures in the scalp, which may stimulate collagen production and improve the absorption of topical treatments like Minoxidil.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections: This treatment uses injections of a concentration of your own platelets into the scalp to encourage hair growth.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: In this surgical procedure, active hair follicles are moved from a dense area of the scalp (like the back of the head) to thinning areas.
How to Prevent Hair Thinning
While some causes of hair loss are outside your control, certain lifestyle adjustments can help maintain your hair’s health and prevent unnecessary shedding.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Ensure your meals are rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals. Foods like leafy greens, nuts, fish, and beans provide essential nutrients for strong hair.
- Be Gentle with Your Hair: Avoid harsh chemical treatments and limit the use of heat styling tools. Opt for loose hairstyles to reduce tension on your hair follicles. Use a wide-tooth comb to gently detangle wet hair.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or regular exercise into your routine.
- See a Doctor Early: If you notice signs of hair thinning—like a wider part, a smaller ponytail, or more hair falling out than usual—consult a dermatologist as soon as possible. Early intervention can make a significant difference.
Your Next Steps to Healthier Hair
Dealing with thinning hair can be a journey, but it’s one you don’t have to navigate alone. The key is to start by identifying the underlying cause with the help of a healthcare professional. From there, you can explore the many effective treatments and lifestyle changes available.
By taking a proactive approach—eating a nutritious diet, managing stress, and being gentle with your hair—you can create a strong foundation for healthy hair growth. Remember, seeking professional advice is the most reliable step toward finding a solution that works for you and restoring both your hair and your confidence.